Receptor Cards
:focus(733x200:734x201))
An educational resource for Pharmacology
We have developed a new teaching resource to assist learning in pharmacology and pharmacy education. Supported by a British Pharmacological Society teaching award Dr Stokes & Dr Norton have piloted the use of the cards in undergraduate teaching classes and presented their findings at Pharmacology 2018.
The ReceptorCards are a pocket-sized pack of flash cards covering the major families of receptors and signalling proteins. For each family of receptors there is a general card (colour coded) and a collection of important receptors from each family; 42 cards cover GPCRs, ion channels, nuclear receptors, enzymes, and transporters. Key facts are included on the rear of the cards covering signalling, expression, agonists and antagonists. In addition, the set of ReceptorCards includes a complementary pack of SignallingCards (34 cards). These cover the main intracellular signalling proteins (e.g. cAMP, Gs, adenylate cyclase…) allowing students to “map” out the pathways in front of them. Key facts are listed on the rear of the cards in quiz form allowing students to test themselves or each other.
The cards feature cartoon drawings of receptors and proteins allowing students to see how they can be represented if they are asked to draw and label a receptor.
For students: if you are studying pharmacology in your degree you might find these ReceptorCards to be a useful resource for revision.
For educators: teaching pharmacology or cell signalling, the ReceptorCards can be a useful addition to online material/textbooks. For ideas on implementing their use in lectures/workshops please email l.stokes@uea.ac.uk.
Please note that we are unable to supply these cards until further notice.
The full pack of ReceptorCards are printed on a durable never-tear material.
For bulk purchases (>5 packs) or purchasing via a purchase order number please contact l.stokes@uea.ac.uk for a customised quotation.
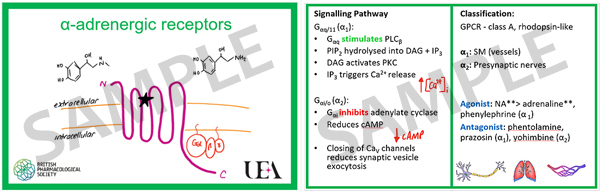
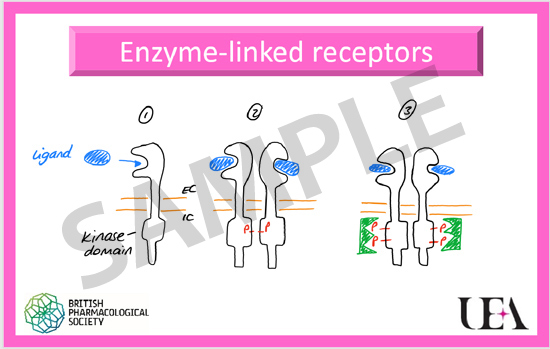
Each pack contains the following cards:
| Receptor Cards | Signalling Cards |
|---|---|
| GPCR | Adenylate cyclase |
| Muscarinic receptors | AMP_activated protein kinase |
| Beta adrenergic receptors | Ca2+ |
| Alpha adrenergic receptors | Calmodulin |
| Histamine receptors | cAMP |
| P2Y receptors | DAG |
| GABA B receptors | Depolarisation |
| Serotonin receptors | Dimersation |
| Dopamine receptors | Galpha i/o |
| Glutamate receptors | Galpha q/11 |
| Opioid receptors | Galpha s |
| Enzyme-linked receptors | Galpha 12/13 |
| EGFR | G beta/gamma |
| TGF receptor | Heat shock proteins |
| Cytokine receptor | Hormone response element |
| Insulin receptor | Hyperpolarisation |
| Nuclear receptors | Inositol triphosphate IP3 |
| Glucocorticoid receptor | K+ |
| Mineralcorticoid receptor | MAPK cascade |
| Thyroid hormone | Na+ |
| PPAR | Phosphoinositide3-Kinase (PI3K) |
| Transporters | PIP2 |
| H+K+ ATPase | Phospholipase C (PLC) |
| Na+K+ ATPase | PKA |
| Ca2+ ATPase | Protein kinase C (PKC) |
| SLC6 family (SERT) | Ras |
| SLC2 family (glucose) | Responses |
| SLC5 family (glucose) | Neurotransmitter release |
| Enzymes | Gene expression |
| Cyclooxygenase | Action potential |
| Monoamine oxidase | Muscle contraction |
| Cholinesterase | Muscle relaxation |
| Ion Channels | Secretion |
| AMPA receptors | Cell growth |
| NMDA receptors | Vasoconstriction/Vasodilation |
| IP3 receptors | |
| P2X receptors | |
| Nicotinic receptors | |
| Cav channels | |
| Kv channels | |
| Nav channels | |
| 5HT3 receptors |